Head-Actuator Assembly
We often call the Head-Actuator Assembly as head stacks or only heads for short. In fact, we make a mistake in some way. Let’s take a look at a head-actuator Assemble on the flowing photo:
Mostly, each platter is accessed for read /write operations using two read/write heads, one mounted on the top of the platter and another on the bottom. These heads are mounted onto arms that allow them to be moved from the outer tracks of the hard drive to the inner tracks and back again. The arms are controlled using a device called an actuator that positions the arms to the appropriate track on the disk. The read/write heads don’t touch the platter when the platter is spinning at full speed; instead, they float on an extremely thin cushion of air (10 millionths of an inch, Winchester disk drive). That’s why power surge may cause Head crash and platter scratch due to the fast rotating rolling of platters.
Notice: In 1973, IBM introduced the IBM 3340 “Winchester” disk drive, the first significant commercial use of low mass and low load heads with lubricated media. All modern disk drives now use this technology and/or derivatives thereof. Project head designer/lead designer Kenneth Haughton named it after the Winchester 30-30 rifle after the developers called it the “30-30” because of it was planned to have two 30 MB spindles; however, the actual product shipped with two spindles for data modules of either 35 MB or 70 MB.
How they work?
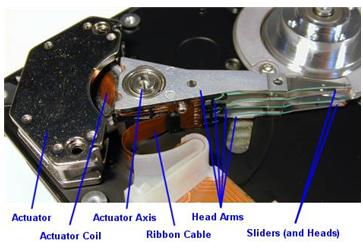
The hard disk platters are accessed for read and write operations using the read/write heads mounted on the top and bottom surfaces of each platter. Obviously, the read/write heads don’t just float in space; they must be held in an exact position relative to the surfaces they are reading, and furthermore, they must be moved from track to track to allow access to the entire surface of the disk. The heads are mounted onto a structure that facilitates this process. Often called the head assembly or actuator assembly (or even the head-actuator assembly), it is comprised of several different parts.
The heads themselves are mounted on head sliders. The sliders are suspended over the surface of the disk at the ends of the head arms. The head arms are all mechanically fused into a single structure that is moved around the surface of the disk by the actuator. (Sort of like “the wrist connected to the hand”, why I say it is a hand because it is very skillful and ingenious and the upper site is Arm: D).They play an important role in the function and performance of the drive. In particular, advances in slider, arm and actuator design are critical to improving the seek time of a hard disk.