How to configure a WD EIDE hard drive using the Alternate Jumper Settings?
When NOT to use Alternate Jumper Settings:
* If you are running Windows 2000/XP/Vista.
* If the system can boot with just one jumper on the drive without locking up.
* If the drive is installed on an IDE controller card that is providing support to access the full drive capacity.
When to use Alternate Jumper Settings
The most common scenario when a drive should be configured with the Alternate Jumper Settings is when the system hangs up or freezes upon boot up after auto-detecting all IDE devices. The reason for this error is because the drive capacity is larger than what the system can support.
What happens after the drive is configured with the Alternate Jumper Settings
The full capacity of the drive is not recognized. In order for the system to boot properly, the BIOS will recognize smaller drive capacity. Depending on your BIOS, your drive will recognize one of the following sizes: 2.1GB, 8.4GB, 32GB.
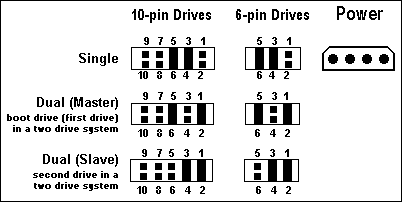
Configuring a single (alone on the IDE cable) drive with the Alternate Jumper Settings
If you are connecting your drive as the only IDE device on the cable, place the jumper shunts on pins 3 & 4 and 5 & 6. Connect the drive to the black connector at the end of the cable.
Configuring a primary or dual Master drive with the Alternate Jumper Settings
If you are connecting your drive as the Master drive on the cable with another IDE device, place the jumper shunts on pins 1 & 2 and 5 & 6. Then configure the jumper on the other IDE device as Slave. Connect the Master drive to the black connector at the end of the cable and the Slave device to the gray connector located at the middle of the cable.
Configuring a secondary or dual Slave drive with the Alternate Jumper Settings
If you are connecting your drive as the Slave drive on the cable with another IDE device, place the jumper shunts on pins 1 & 2 and 3 & 4. Then configure the jumper on the other IDE device as Master. Connect the drive to the gray connector at the middle of the cable and the other IDE device to the black connector located at the end of the cable.