
5 Popular Data Recovery Freewares
Pandora Recovery
Find, preview and restore permanently deleted files.
Operating system: Windows 2000/XP/Vista
 Pandora Recovery is a powerful free tool that provides its users an effective way to attempt recovery of permanently deleted files. And that does not mean restoration of a file from Recycle Bin. The software recovers files removed from Recycle Bin, deleted using Shift + Delete keys bypassing Recycle Bin and files deleted from DOS prompt. Pandora Recovery lets its user browse, search, preview and recover files deleted from NTFS and FAT volumes, supporting hard drives, flash drives and memory cards. It successfully handles archived, hidden, encrypted and compressed files and recovers Alternate Data Streams (ADS). Pandora Recovery features classic interface wizards, hints and context-sensitive help. Pandora Recovery allows user to browse and search the tree of deleted files where show deleted items only button comes handy. Finally, it has ability to scan drive clusters, picking up files whose MFT record has been reused by OS, damaged or recreated (it can restore files on formatted drives).
Pandora Recovery is a powerful free tool that provides its users an effective way to attempt recovery of permanently deleted files. And that does not mean restoration of a file from Recycle Bin. The software recovers files removed from Recycle Bin, deleted using Shift + Delete keys bypassing Recycle Bin and files deleted from DOS prompt. Pandora Recovery lets its user browse, search, preview and recover files deleted from NTFS and FAT volumes, supporting hard drives, flash drives and memory cards. It successfully handles archived, hidden, encrypted and compressed files and recovers Alternate Data Streams (ADS). Pandora Recovery features classic interface wizards, hints and context-sensitive help. Pandora Recovery allows user to browse and search the tree of deleted files where show deleted items only button comes handy. Finally, it has ability to scan drive clusters, picking up files whose MFT record has been reused by OS, damaged or recreated (it can restore files on formatted drives).
Version 2.1.1 supports Data carving (surface scan) of Adobe PhotoShop PSD and MS Outlook PST.
EASEUS Data Recovery Wizard Free Edition
Recover data from formatted/lost partitions.
Operating system: Windows 2000/XP/2003/Vista/Server 2008/7
EASEUS Data Recovery Wizard Free Edition is a one-stop & free data recovery software to recover 1 GB data free of charge. It is a comprehensive file recovery freeware which can recover deleted files or folders even when they have been emptied from Recycle Bin, recover data due to format, lost partition, system crash, and virus attack. Compare with other data recovery freeware, it can restore files from formatted disk, dynamic disk, deleted or lost partition with original file names & storage paths. By the way, it is designed with wizard mode which makes the data recovery process easy even for a beginner. Free, easy-to-use, powerful functions make EASEUS Data Recovery Wizard Free Edition a must-have data recovery software in case of any data loss.
PC Inspector File Recovery
Recover lost or damaged files.
Operating system: Windows 95/98/Me/2000/XP/NT
PC Inspector File Recovery is a data recovery program that supports the FAT 12/16/32 and NTFS file systems. Finds partitions automatically, even if the boot sector or FAT has been erased or damaged (does not work with the NTFS file system). Recovers files with the original time and date stamp. Supports the saving of recovered files on network drives.
Version 4 supports the saving of recovered files on network drives.
Data Recovery
Restore accidentally deleted FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, and NTFS files.
Operating system: Windows 95/98/Me/2000/XP/Vista/NT
FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, NTFS undeletion. Undelete NTFS compressed files. Undelete EFS encrypted files. Wipe out deleted files never to be recovered again. Runnable from floppy disk. Search by partial string in the file name. Undelete whole files in a directory. Neither installation nor DLLs is needed. Windows Vista supported.
R-Linux Free Recovery
Recover files from existing logical disks when file records are lost.
Operating system: Windows 95/98/Me/2000/XP/Vista/NT
R-Linux is a free data recovery and undelete utility for Ext2FS/3FS (Linux) file systems. File recovery after power failure, system crash, virus infection or partition reformation, even for the different file system. Unformat and unerase tool. The utility creates image files an entire disk, partition or its part. Such drive image can be processed like regular drive. Recognition and parsing of Dynamic (Windows 2000/XP), Basic and BSD (UNIX) partitions layout schema. Localized names support. Recovered files can be saved on any (including network) disks accessible by the host operating system.
Version 3.0 may include unspecified updates, enhancements, or bug fixes.



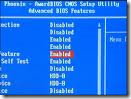 The BIOS is a program pre-installed on computers (with the exception of Macs) that the computer uses to start up. The CPU accesses the BIOS before the operating system is loaded. The BIOS then checks all your hardware connections and locates all of your devices. If everything is OK, the BIOS loads the operating system into the computer’s memory and finishes the boot-up process.
The BIOS is a program pre-installed on computers (with the exception of Macs) that the computer uses to start up. The CPU accesses the BIOS before the operating system is loaded. The BIOS then checks all your hardware connections and locates all of your devices. If everything is OK, the BIOS loads the operating system into the computer’s memory and finishes the boot-up process.

 Data recovery services for faulty hard disk drives in Sydney and Melbourne, Australia.
Data recovery services for faulty hard disk drives in Sydney and Melbourne, Australia. DOS and DOS based programs like Windows 3.x and Windows 95 cannot access drives over 1024 cylinders on their own, but require third party assistance to use large hard drives. SCSI drives handle this with drivers built in to the SCSI controller, so we will limit this discussion to ATA hard drives. There are several methods used to overcome the cylinder limitation, and all of them involve translation.
DOS and DOS based programs like Windows 3.x and Windows 95 cannot access drives over 1024 cylinders on their own, but require third party assistance to use large hard drives. SCSI drives handle this with drivers built in to the SCSI controller, so we will limit this discussion to ATA hard drives. There are several methods used to overcome the cylinder limitation, and all of them involve translation.

